Understanding Sickle Cell Disease: Raising Awareness and Promoting Support
What is Sickle Cell Disease?
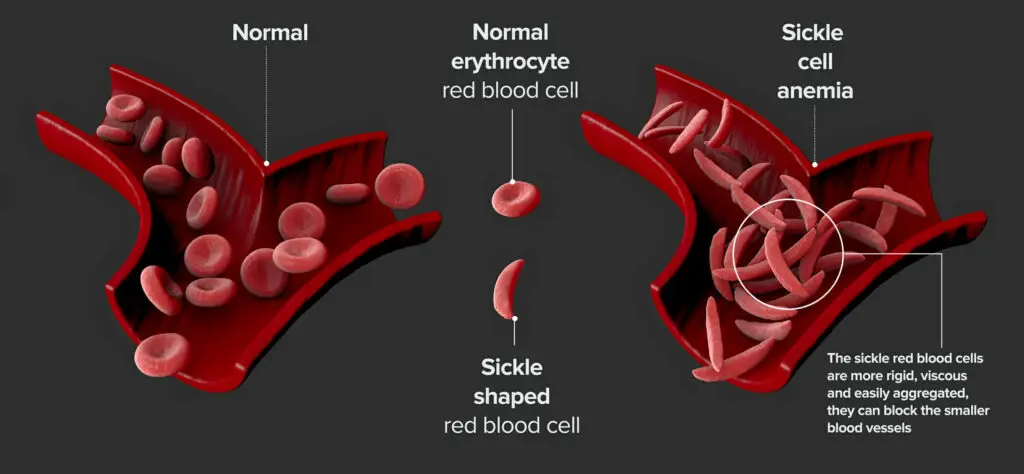
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a genetic blood disorder that affects millions of people worldwide, particularly those of African, Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, and South Asian descent. The condition arises from a mutation in the gene responsible for hemoglobin production, the crucial protein within red blood cells that facilitates oxygen transport throughout the body. This mutation leads to the production of abnormal hemoglobin known as hemoglobin S (HbS), which causes red blood cells to become rigid and assume a sickle or crescent shape under certain conditions.
Symptoms and Complications
Individuals with sickle cell disease may experience a wide range of symptoms and complications, including:
- Pain Crises: Episodes of severe pain, often referred to as pain crises or vaso-occlusive crises, occur when sickle-shaped red blood cells block blood flow to tissues and organs.
- Anemia: Sickle cell disease can cause chronic anemia due to the premature destruction of red blood cells.
- Infections: People with sickle cell disease are at increased risk of infections, particularly those caused by bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Organ Damage: Prolonged episodes of reduced blood flow can lead to organ damage, including damage to the spleen, kidneys, lungs, and brain.
- Stroke: Children with sickle cell disease are at increased risk of stroke due to blockages in the blood vessels supplying the brain.
- Acute Chest Syndrome: A potentially life-threatening complication characterized by chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing, often requiring hospitalization.
Treatment and Management
While there is currently no cure for sickle cell disease, various treatment options and management strategies are available to help alleviate symptoms and reduce complications. These may include:
- Pain Management: Medications and supportive therapies to manage pain during acute crises.
- Hydroxyurea: A medication that can reduce the frequency of pain crises and complications in some individuals with sickle cell disease.
- Blood Transfusions: Transfusion therapy may be used to treat severe anemia or prevent complications such as stroke.
- Bone Marrow Transplantation: A potential curative treatment option for select individuals with sickle cell disease.